ADVERTISEMENTS:
Model Sociology Solved Test Papers for Civil Services Exams!
1. Man, for the first time, became tool maker during the
(a) Paleolithic age
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Mesolithic age
(c) Chalcolithic age
(d) Neolithic age
Ans. (a)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Which one of the following is an integration of matter and concomitant dissipation of motion, during which matter passes from a definite coherent homogeneity to an indefinite incoherent heterogeneity?
(a) Development
(b) Evolution
(c) Growth
(d) Progress
Ans. (b)
3. Auguste Comte maintained that human knowledge passed through three major stages, which are- positive, metaphysical, theological.
Identify the correct order of their emergence using the codes given below:
(a) Theological, Metaphysical, Positive
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Metaphysical, Theological, Positive
(c) Theological, Positive Metaphysical
(d) Positive, Theological, Metaphysical
Ans. (a)
4. Consider the following statements about culture:
1. Each culture is holistic.
2. Cultural complex is the smallest unit of culture.
3. Culture is shared by the members of a given group.
4. Physical and biological features of people are determined by culture.
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2 and 4
Ans. (c)
5. According to Linton, which of the following classes of traits are found in a culture?
(a) Specialities, alternatives and configurations
(b) Universals, specialities and alternatives
(c) Configurations, universals and patterns
(d) Alternatives, patterns and configurations
Ans. (b)
6. When the members of a group have a belief that they are in some way superior to all who are members of other groups, it is a case of
(a) Ethnicity
(b) Ethnocentrism
(c) Ethnic group
(d) Ego-centrism
Ans. (b)
7. A peaceful co-existence of distinct ethnic groups in a society is called
(a) Integration
(b) Assimilation
(c) Amalgamation
(d) Cultural Pluralism
Ans. (d)
8. When a whole way of life is in the process of change under the influence of another culture, we call it
(a) Acculturation
(b) Diffusion
(c) Assimilation
(d) Socialisation
Ans. (c)
9. Consider the following theories-
1. Comte’s theory of positivism
2. Durkheim’s theory of division of labour
3. Spencer’s theory of organic analogy
The correct chronological sequence of the above theories is:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 3 and 2
(c) 3, 1 and 2
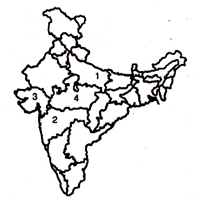
(d) 2, 1 and 3
Ans. (b)
10. A pattern of behaviour organised around specific rights and duties that are associated with a particular social position is called-
(a) Role
(b) Status
(c) Prestige
(d) Power
Ans. (a)
11. Which one of the following Acts removed the restriction on gotra marriage?
(a) The Hindu Marriage Validity Act, 1949
(b) The Special Marriage Act, 1954
(c) The Hindu Marriage Disabilities Removal Act, 1946
(d) The Hindu Marriage Act, 1955
Ans. (a)
12. Ultimogeniture is the rule whereby
(a) The first-born child succeeds to the estate of the father/mother
(b) The last-born child succeeds to the estate of the father/mother
(c) The surviving descendant takes over the family property
(d) The sons claims absolute rights over the family property excluding the daughters
Ans. (b)
13. The correct order of the main objectives of marriage in the traditional Hindu Society is
(a) Praja, Rati and Dharma
(b) Rati, Dharmaand Praja
(c) Dharma, Rati and Praja
(d) Dharma, Praja and Rati
Ans. (d)
14. Opposition to which one of the following was the primary goal of the Kheda movement of Gujarat (1919)?
(a) Taxes
(b) Sudden price rise
(c) Money lending class
(d) Unpaid forces labour
Ans. (a)
15. Assertion (A)- Socially sanctioned sex gratification is a basis for marriage.
Reason (R)- Marriage regulates sexual relations between individuals.
(a) Both R and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
16. Consider the following statements:
1. Equal access to property, power and prestige ends up in social stratification
2. Differential access to property, power and prestige ends up in social stratification.
3. Unequal access to property, power and prestige ends up in social stratification
Which of these statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
Ans. (c)
17. Who pointed out that social stratification is needed to ensure effective role allocation and role of performance?
(a) Moore and Parsons
(b) Davis and Parsons
(c) Parsons and Weber
(d) Davis and Moore
Ans. (d)
18. Which one of the following represents a form of differentiation and not stratification?
(a) Class
(b) Gender
(c) Caste
(d) Sex
Ans. (d)
19. Consider the following statements- Functionalist theory of stratification states that
1. Social stratification is a necessity.
2. Every society must select among individual members to fill wide variety of social positions.
3. In order to attract the most talented individual to each position, society must set up a system of differential rewards
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 2
Ans. (c)
20. The four functional group that came into being in the Varna system such as teaching and preaching, administration and protection, agriculture and commerce and services and manual labour are the result of the need for
(a) Division of social living
(b) Division of gender
(c) Division of social categories
(d) Division of labour
Ans. (a)
21. Crony capitalism is dominated by
(a) Medium scale industries
(b) Powerful business families
(c) Partnership companies
(d) Group of powerful land owners practising mechanised farming
Ans. (c)
22. Consider the following:
1. Collective action
2. Leadership
3. Ideology
4. Restoration of equilibrium
5. Interest
Features concerning a social movement are:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5
(b) 2, 3, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 4 and 5
Ans. (a)
23. Ogburn’s idea that change first occurs in the material technology is borrowed
(a) Directly from Marx and indirectly from Saint Simon and Condorcet
(b) Directly from Saint Simon and indirectly from Marx
(c) Directly from Condorcet and indirectly from Marx
(d) Directly from Gabriel Trade
Ans. (b)
24. Consider the following statements:
A caste is said to be dominant when it
1. is numerically preponderant.
2. claims ritual purity
3. is political powerful
4. owns most of the land in a village
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (d)
25. Disparity in income levels of different economic entities are measured on:
(a) Supply curve
(b) Demand curve
(c) Cost curve
(d) Lorenz curve
Ans. (d)
26. Who coined the term ‘folk-urban continuum’?
(a) RE. Park
(b) R. Redfield
(c) R. Dahrendorf
(d) B.K. Malinowski
Ans. (b)
27. Who among the following said that “industries are the Temples of Modern India”?
(a) Ambedkar
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) S. Radhakrishnan
Ans. (b)
28. The term ‘Gentrification’ is applied to the kind of urban growth.
(a) When migrants from abroad start living
(b) Where there is urban revival of stylish neighbourhood
(c) Where marginalised groups begin to live
(d) Where elderly people live
Ans. (c)
29. Consider the following concepts:
1. Culture of poverty
2. Urbanism as a way of life
3. Sector theory
4. Folk-urban continuum
5. Global city
The correct chronological sequence of the above concepts is:
(a) 1, 3, 2, 5 and 4
(b) 3, 1, 2, 4 and 5
(c) 3, 2, 4, 1 and 5
(d) 1, 3, 2, 4 and 5
Ans. (c)
30. What is the first and foremost criterion for defining town?
(a) Density of population
(b) Higher percentage of employment in non-agricultural activities
(c) High literacy rate
(d) Presence of slums
Ans. (b)
31. Consider the following statements:
In a pre-modern political system, leaders win support for exercising authority through-
1. Benefitting followers with their success.
2. Causing succession in the ranks of opponents
3. Threatening to withdraw advantages.
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
Ans. (a)
32. Consider the following:
1. Ligality
2. Regularity
3. Violence
4. Will
Part and parcel of legitimacy includes:
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (b)
33. Political modernisation is a multifaceted process involving changes in all areas of human thought and activity as viewed by
(a) C.E. Welch (Jr.)
(b) Benjamin Schwartz
(c) Hutington
(d) Paul Brass
Ans. (c)
34. The process of acquisition of a political culture is known as:
(a) Political modernisation
(b) Political socialisation
(c) Political stratification
(d) Political legitimation
Ans. (b)
35. Consider the following statements: Political modernisation goes hand in hand with
1. Illiteracy
2. Political participation
3. Urbanisation
4. Use of mass media
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans. (d)
36. Consider the following statements- Authority consists of-
1. Legitimacy
2. Qualification
3. Power
4. Regularity
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
37. Assertion (A)- In order to survive, an authoritarian State resorts to repression, permanent mobilisation and manipulation.
Reason (R)- In an authoritarian State, the bureaucratic apparatus becomes responsive to the needs of the masses.
(a) Both R and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (c)
38. In the interest of the tribals, which one of the following Schedules of the Constitution of India gives powers to the Governor of every State that has Scheduled Areas?
(a) Fifth Schedule
(b) Eighth Schedule
(c) Fourth Schedule
(d) Third Schedule
Ans. (a)
39. Which of the following Articles in the Constitution of India explicitly guarantee the protection of the interests of minorities in India?
(a) Articles 27 and 28
(b) Articles 29 and 30
(b) Articles 31 and 32
(d) Articles 33 and 34
Ans. (b)
40. What percentage of women beneficiaries has been targeted under the Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP)?
(a) 35%
(b) 15%
(c) 20%
(d) 30%
Ans. (a)
41. Spencer viewed all evolution in terms of two types of society, the
(a) Agrarian and industrial
(b) Military and industrial
(c) Pastoral and industrial
(d) Tribal and industrial
Ans. (b)
42. Assertion (A): Altruistic suicides occur more in over- integrated societies.
Reason (R): Suicide is the desperate act of an individual.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but is R true.
Ans. (b)
43. Assertion (A): New technology is received more quickly than values.
Reason (R): Changes in non-material culture always lag behind changes in material culture.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but is R true.
Ans. (a)
44. Assertion (A): It is witnessed that even the rational persons put some food and eatables on the burial pit of dead persons.
Reason (R): Modes of action persist more obstinately than the modes of thinking.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but is R true.
Ans. (a)
45. Assertion (A): In a given society, the rate of suicide is significantly higher in cities than in villages.
Reason (R): Autonomy of individual increases with increasing social division of labour.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but is R true.
Ans. (b)
46. Assertion (A): There is a proliferation of voluntary associations in cities.
Reason (R): The hold of collective consciousness declines with an increase in organic solidarity.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but is R true.
Ans. (a)
47. A musician singing at a concert is an example of
(a) Act
(b) Action
(c) Process
(d) Collective behaviour
Ans. (b)
48. According to Parsons, prostitutions is a case of
(a) Deviance
(b) Secondary institution
(c) Institutionalisation
(d) Adoption
Ans. (b)
49. Which one of the following can be referred to as independently defined role?
(a) Father
(b) Teacher
(c) Painter
(d) Officer
Ans. (c)
50. The correct sequence of early stages of socialisation as developed by Erik Erikson is
(a) Trust vs. Mistrust, Autonomy vs. Doubt, Initiative vs. Guilt, Industry vs. Inferiority
(b) Initiative vs. Guilt, Trust vs. Mistrust, Autonomy vs. Doubt, Industry vs. Inferiority.
(c) Trust vs. Mistrust, Initiative vs. Guilt, Autonomy vs. Doubt, Industry vs. Inferiority
(d) Initiative vs. Guilt, Industry vs. Inferiority, Autonomy vs. Doubt, Trust vs. Mistrust
Ans. (a)
51. The process whereby various structural components of a social system are organised is called:
(a) Assimilation
(b) Integration
(c) Cooperation
(d) Accommodation
Ans. (b)
52. What percentage of women beneficiaries has been targeted under the Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP)?
(a) 35%
(b) 15%
(c) 20%
(d) 30%
Ans. (a)
53. The community “is the smallest territorial group that can embrace all aspects of social life” according to:
(a) C.H. Cooley
(b) Kingsley Davis
(c) R.M. Maclver
(d) Harry H. Johnson
Ans. (b)
54. Promised rewards for compliance and threatened penalties for non-compliance with group expectations, is called:
(a) Norms
(b) Values
(c) Sanctions
(d) Mores
Ans. (c)
55. Which one of the following concepts correctly refers to the process by which cultural traits are transmitted from one society to another?
(a) Acculturation
(b) Universalisation
(c) Diffusion
(d) Assimilation
Ans. (b)
56. Who among the following defined ‘function’ as the contribution of a part to the maintenance and well being of the whole?
(a) Malinowski
(b) Emile Durkheim
(c) Herbert Spencer
(d) Radcliffe-Brown
Ans. (d)
57. A society in which cultural groups are not forced into assimilation, but are able to coexist with one another in mutual respect and with a fair share of the national resources is described as
(a) A melting pot
(b) Democratic
(c) Pluralistic
(d) A mosaic
Ans. (b)
58. The assumption that every culture needs to be evaluated on its own terms, is the converse of
(a) Enculturation
(b) Ethnocentrism
(c) Domination
(d) Minoritism
Ans. (b)
59. According to Parsons, for a social structure to persist, it must perform which of the following functions?
1. Adaptation
2. Social action
3. Integration
4. Socialisation
5. Goal attainment
6. Pattern maintenance
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 5 and 6
(d) 1, 2, 4 and 5
Ans. (c)
60. Who among the following identified four major types of cooperation, that is, spontaneous, traditional, directed and contractual?
(a) Lewis Coser
(b) George Simmel
(c) Robert Nisbet
(d) George C. Homans
Ans. (c)
61. Which one of the following was believed to represent the vertical unit of castes?
(a) Varna system
(b) Jajmani system
(c) Sanskritisation
(d) Endogamy
Ans. (a)
62. Whose theory of social change holds that “Do not say that social movement excludes political movement. There is never a political movement which is not at the same time social?”
(a) Marx
(b) Morgan
(c) Montesquieu
(d) Vico
Ans. (c)
63. Oswald Spengler has discussed the rise and fall of eight civilisations of the world.
Which among the following is not discussed by him?
(a) Egyptian
(b) Roman
(c) Mesopotamian
(d) Classical Chinese
Ans. (c)
64. Assertion (A): There is an increasing trend among educated women to get employment as an assertion of their new identity and to provide economic support to the family.
Reason (R): Employment of women leads to more stress and strain between job roles and family roles resulting in role-conflict.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (b)
65. Consider the following statements:
According to the Imperial Gazetteer of India, a tribe is a-
1. Collection of families with a common name
2. Community using ancient means of production
3. Community speaking a common dialect
4. Community which is usually exogamous
5. Community occupying a common territory
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 5
(d) 1, 3 and 5
Ans. (a)
66. With whose name would one associate the study of the economy of Trobriand Islanders?
(a) J.P.S. Uberoi
(b) E. Evans Pritchard
(c) B. Malinowski
(d) R. Firth
Ans. (c)
67. The correct sequence in descending order of the total population of Scheduled Tribes in the States marked on the map is:
(a) 4, 2, 1 and 3
(b) 4, 2, 3 and 1
(c) 2, 4, 1 and 3
(d) 2, 4, 3 and 1
Ans. (b)
68. Which one of the following types of societies does Alvin Toffler discuss in the Third Wave?
(a) Industrial society
(b) Post-Industrial society
(c) Information society
(d) Cultural modernism
Ans. (b)
69. Who among the following has given the tribe-caste continuum model to explain the process of tribal assimilation?
(a) M.N. Srinivas
(b) Surajit Sinha
(c) S.C. Dube
(d) D.N. Majumdar
Ans. (d)
70. Who among the following gave the suggestion of ‘National Park to the Government for tribal development in India?
(a) GS. Ghurye
(b) D.N. Majumdar
(c) N.K. Bose
(d) Verrier Elwin
Ans. (d)
71. Mahmood Mamdani regards high fertility patterns amongst the poor as:
(a) Normal
(b) Abnormal
(c) Rational
(d) Irrational
Ans. (c)
72. The first synchronic all India Census was organised in the year:
(a) 1871
(b) 1872
(c) 1901
(d) 1951
Ans. (b)
73. Consider the following States:
1. Kerala
2. Uttar Pradesh
3. Madhya Pradesh
4. Punjab
The correct sequence of these states in descending order in terms of sex-ratios (females per thousand males as per 1991 Census) of their population is-
(a) 3, 1, 2 and 4
(b) 3, 1, 4 and 2
(c) 1, 3, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3, 4 and 2
Ans. (c)
74. ‘Look after the population and the population will look after itself.” This slogan emerged in World population Conference held at:
(a) Belgrade
(b) Alma Ata
(c) Bucharest
(d) Cairo
Ans. (d)
75. The distribution of human settlements in terms of rural and urban constitutes:
(a) A dichotomy
(b) A continuum
(c) A dialectical system
(d) Urban development
Ans. (a)
76. Which one of the following is the correct arrangement of the States marked in the given map in terms of ascending order of the levels of urbanisation?
(a) 2, 1, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 1, 4 and 3
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2, 4 and 3
Ans. (b)
77. The census definition of town remained more or less the same for a very long period in India. This was modified at the national level in the year
(a) 1961
(b) 1971
(c) 1981
(d) 1991
Ans. (a)
78. Assertion (A): As less developed countries begin to industrialise, their cities also expand.
Reason (R): Industrialisation is a necessary condition of urban growth.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
79. Consider the following countries:
1. Pakistan
2. India
3. Indonesia
4. Bangladesh
The correct sequence of those countries in descending order in terms of their Muslim population is
(a) 2, 3, 4 and 1
(b) 3, 2, 4 and 1
(c) 3, 2, 1 and 4
(d) 2, 3, 1 and 4
Ans. (c)
80. “Ad-hocracy” is the system whereby there will be an administrative system with transient project teams, task forces and ad hoc committees which would give dynamism and replace bureaucracies. This term was coined by:
(a) Peter Blau
(b) A. Etzioni
(c) Alvin Toffler
(d) Goldthorpe
Ans. (c)
81. Assertion (A): In capitalist system of production, class conflict is inevitable which is much better than economic competition and bargaining.
Reason (R): Class conflict is the only source of institutional change.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans. (c)
82. The Politics of Untouchability by O.M. Lynch was a study representing the socio-economic and political mobility of which of the following?
1. Nadars of Tamil Nadu
2. Jatavs of Agra
3. Mahars of Maharashtra.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b)
83. Which of the following is correct?
1. Succession refers to transmission of office.
2. Inheritance refers to transmission of office.
3. Succession refers to “transmission of property.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) None of the above
Ans. (a)
84. The term ‘class’ signifies conflict groups that are generated by the differential distribution of authority in imperatively coordinated association that is organisation in which orders are given and taken.
Who among the following has explained class in this way?
(a) K. Marx
(b) C.W. Mills
(c) L. Coser
(d) R. Dahrendorf
Ans. (d)
85. Studies on jajmani system address to which of the following?
1. Type of relationships and reimbursement.
2. Relative magnitude of traditional economic interaction.
3. Kind of ecological unit appropriate for a study of economic interaction.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans. (b)
86. What specific interpretation has been given by T. Beidelman in respect of the jajmani system of Indian traditional society?
(a) Jajmani system provides socio-religious interdependence among the castes
(b) Jajmani system provides interchange of good and services among the castes
(c) Jajmani system provides welfare and economic interdependence among the castes
(d) Jajmani system provides exploitative mechanism whereby upper castes exploit lower castes
Ans. (d)
87. What percentage of women beneficiaries has been targeted under the Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP)?
(a) 35%
(b) 15%
(c) 20%
(d) 30%
Ans. (a)
88. Which of the following Articles in the Constitution of India explicitly guarantee the protection of the interests of minorities in India?
(a) Articles 27 and 28
(b) Articles 29 and 30
(b) Articles 31 and 32
(d) Articles 33 and 34
Ans. (b)
89. Who among the following has stressed that tribe should be defined in terms of a continuum, of which at the one end are tribes and at the other end are the castes?
(a) David Mandelbaum
(b) RG Bailey
(c) N. K. Bose
(d) M. N. Srinivas
Ans. (b)
90. In the interest of the tribals, which one of the following Schedules of the Constitution of India gives powers to the Governor of every State that has Scheduled Areas?
(a) Fifth Schedule
(b) Eighth Schedule
(c) Fourth Schedule
(d) Third Schedule
Ans. (a)
91. Which one of the following statements in respect of status is not correct?
(a) Status is the rank-order position
(b) Status is a position in the general institutional system
(c) Status is the worth of a person as estimated by a group
(d) Status is a cultural attribute of an individual
Ans. (d)
92. Which one of the following statements is correct? The concept of social role, according to E. Goffman has originated in a
(a) Theatrical setting
(b) Social life
(c) System of social stratification
(d) The process of role adaptation
Ans. (b)
93. Political modernisation is a multifaceted process involving changes in all areas of human thought and activity as viewed by
(a) C.E. Welch (Jr.)
(b) Benjamin Schwartz
(c) Hutington
(d) Paul Brass
Ans. (c)
94. Who regards deviance as functional for society?
(a) A. Cohen
(b) E. Durkheim
(c) R.K. Merton
(d) L.K. White
Ans. (b)
95. What does law in a society mean?
1. To transform informal social norms into formal ones
2. To elevate vague obligations and privileges into rights and duties
3. A realm of formal obligation
4. A fear imposed on people to avoid certain actions
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
96. Consider the following factors about socialisation, as conceived by Sigmund Freud:
1. ‘Super-ego’ develops in an individual when the latter assimilates his/her parent’s ideas of right and wrong
2. The rational part of the individual’s ‘id’ takes the form of ego
3. The individual’s organism contacts the external world
4. Innate tendencies, stored in the ‘ id’ seek satisfaction in the external world
Which one of the following is the correct sequence of the factors given above?
(a) 2, 1, 4 and 3
(b) 4, 3, 2 and 1
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 1
(d) 4, 1, 2 and 3
Ans. (b)
97. What is the process, under which one culture merges itself with the dominant culture, called?
(a) Adaptation
(b) Accommodation
(c) Assimilation
(d) Acculturation
Ans. (c)
98. What is the most important and basic factors for social integration according to the functionalists?
(a) Value consensus
(b) Maintenance of relative stability
(c) Structural interdependence
(d) Condition of anomie
Ans. (a)
99. Which one of the following is not covered under the “Element of Social Structure”?
(a) Deviation
(b) Observance
(c) Sanction
(d) Group action
Ans. (a)
100. What are social norms?
(a) Rules whose observance is expected in a society
(b) Laws whose violation invariably leads to punishment
(c) Principles accepted as normal by sociology
(d) Codes which are prescribed in sacred texts
Ans. (a)
101. The number of children under five years of age divided by the number of women between the age group of 15-44 years, multiplied by 1000 is called:
(a) General fertility rate
(b) Crude birth rate
(c) Fertility ratio
(d) Fecundity
Ans. (c)
102. Which one of the following theories refutes the assumption that richness in itself brings down birth rate or in poverty the rate is bound to go up?
(a) Optimum theory of population
(b) Theory of increasing prosperity
(c) Theory of rationalism
(d) Theory of voluntarism
Ans. (a)
103. Consider the following features:
1. Fixed spheres of competence of different offices
2. Charismatic authority
3. Impersonality
4. Recruitment based on merit
Which of these are typical of bureaucratic organisation?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
Ans. (b)
104. Consider the following statements with respect to the pressure groups:
1. They articulate their group interests
2. They exercise their influence on government
3. They safeguard their group interests
4. They bring pressure on general public
Which of these are correct?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
105. Consider the following statements:
In a pre-modern political system, leaders win support for exercising authority through
1. Benefitting followers with their success.
2. Causing succession in the ranks of opponents
3. Threatening to withdraw advantages.
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
Ans. (a)
106. A legitimate right to give certain orders or commands is called:
(a) Power
(b) Authority
(c) Influence
(d) Cohesion
Ans. (b)
107. Illegal activities carried out by professionals and businessmen are called-
(a) Organised crimes
(b) Alienations
(c) Juvenile delinquencies
(d) White collar crimes
Ans. (d)
108. According to Karl Marx, class membership depends upon:
(a) Power
(b) Prestige
(c) Mode of productivity
(d) Productivity relations
Ans. (c)
109. Which of the following types of authorities have been identified by Max Weber?
(a) Rational, emotional and traditional
(b) Rational, charismatic and traditional
(c) Traditional, ideal and rational
(d) Traditional, modern and post-modern
Ans. (b)
110. A body of people having monopoly over the use of force and exercising control within a definite territory is called:
(a) Polity
(b) Government
(c) Nation
(d) State
Ans. (c)