ADVERTISEMENTS:
Unemployment in Rural India!
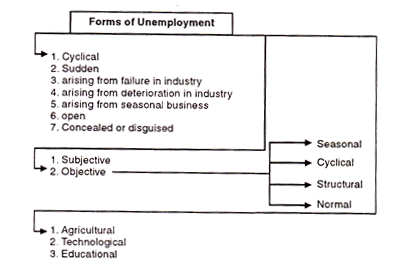
Form of Unemployment # 1. Cyclical Unemployment:
It results from the trade cycle of profit and loss. If there is profit in one time there may be loss in another.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
When there is a depression in trade and business, people are thrown out of work.
Form of Unemployment # 2. Sudden Unemployment:
This happens when there is a sudden change in the employing agencies like corporations, companies. Such changes can be due to unforeseen situations like heavy loss of the organisation or corporation, unexpected fluctuations in the national and international market etc. Due to this people are thrown out of work/job.
Form of Unemployment # 3. Unemployment Arising from Failure in Industry or Business:
Failure in industry or business may be due to less profits, indifferent attitudes of the employer, non-incentives to the employees, negligence of the employers etc. This can lead to unemployment. The employers may be forced to throw some of the employees out of job and retain only those who can keep the industry or business running.
Form of Unemployment # 4. Unemployment Resulting from Deterioration in Industries:
When industries deteriorate due to lack of success in competition or one of the variety of causes, many people become unemployed.
Form of Unemployment # 5. Unemployment Arising from Seasonal Business:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Seasonal business stops when season comes to an end. As a result the people engaged in it are thrown out of work. This seasonal unemployment is inherent also in agricultural sector. This can be caused by the shutting down of seasonal industries like sugar and ice. The work is about six months in a year.
Form of Unemployment # 6. Open Unemployment:
It is a condition in which the people have no work to do. They are able to work and are also willing to work but there is no work for them. This type of unemployment is found mostly in city life.
Form of Unemployment # 7. Concealed or Disguised Unemployment:
This type of unemployment in rural India is 25 percent to 30 percent. It is mostly prevalent among marginal and small fanners. Here, we use the productivity criterion to measure the extent and degree of unemployment.
According to the U.N. Committee of Experts, “the disguisedly unemployed are those persons who work on their own account and who are too numerous relatively to resources with which they work, so that if a number of them were withdrawn to work in other sectors of the economy, the total output of the sector from which they were withdrawn would not be diminished even though no significant reorganization occurred in this sector”.
According to Prof. Nurkse, the marginal productivity of such workers is zero or even negative. In the absence of irrigation facilities, such people look busy in working on their own land, but in fact, they only relieve other members of their family from work. They contribute nothing to agricultural production.
Form of Unemployment # 8. Subjective Unemployment:
This is caused by physical or mental shortcomings of the individual.
Form of Unemployment # 9. Objective Unemployment:
This is caused by factors beyond the control of the individual and it is related to objective circumstances.
Form of Unemployment # 10. Structural Unemployment:
In this case, unemployment is caused because of far-reaching changes either in industry or society. This happens when changes frequently come in the products being produced by a particular industry or because of rapid changes in the society: i.e. social systems, social customs, also in fashions etc.
Form of Unemployment # 11. Normal Unemployment:
It is seen in almost all countries. In a complex economic organisation, it is very difficult to provide employment to every-body.
Form of Unemployment # 12. Agricultural Unemployment: It is seen in Agricultural Sector because of Several Factors:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Drought.
2. Conversion of agricultural’ land into residential plots.
3. Adoption of new methods of agriculture during harvesting and sowing of crops etc.
4. Excessive increase in population.
5. Seasonal nature of agriculture.
Rural unemployment is mainly related with agricultural unemployment. According to the Royal Agricultural Commission, the farmers in the villages of India remain unemployed for three to six months.
According to the report of the National Income Committee published in 1951, the per capital income of people engaged in agriculture was estimated at rupees 180 while the Income of people engaged in agriculture was estimated at two and a half times this figure, i.e. rupees 450.
The cause of this difference in Income is agricultural unemployment. Dr. R.K. Mukerji has estimated that the number of Landless labourers among the people dependent upon agriculture in India is between six and seven crores. The biggest cause of agricultural unemployment is that, in India agriculture is extremely unorganised and diversified.
Form of Unemployment # 13. Technological Unemployment:
It comes from the advancement of technology. It mostly happens in industries when people are displaced by machines.
Form of Unemployment # 14. Educational Unemployment:
This is related to education. When the educated people do not get proper gainful employment, this type is called educational unemployment. This is found in urban areas.