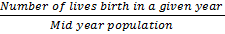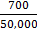ADVERTISEMENTS:
Compilation of 100+ probable sociology GK questions and answers especially compiled for IAS, Civil Service, UGC-NET & UPSC aspirants!
1. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Racial inter-mixture leads to degeneration
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) The concept of pure race is a myth
(c) Inter-mixture of races is universal
(d) No race is superior or inferior to any other race
Ans. (a)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. When inherent superiority of a people over another is legitimised in terms of biological attributes, it is called:
(a) Racism
(b) Ethnicity
(c) Society
(d) Cultural pride
Ans. (b)
3. Consider the following theories:
1. Evolutionist
2. Diffusionist
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Functionalist
4. Phenomenologist
Which of these theories adopt a holistic view of culture?
(a) 1 and2
(b) 2and4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
4. Which one of the following is an example of role-set?
(a) A teacher’s relationship with his pupils, colleagues, the principal and parents
(b) A teacher as husband, father, sportsman and social activist
(c) A teacher becoming later a head of the department, a principal and a registrar
(d) A student becoming a husband, a father and a grandfather over a period of time
Ans. (a)
5. Pronatalism refers to the:
(a) View that a person should not have as many children as possible
(b) View that only the child can provide sustenance and salvation to the family
(c) Strong positive value a society places on having children
(d) View that vitality of the family depends upon the strong physique of the child
Ans. (c)
6. The view that without using the values of one’s own culture to judge all others is known as:
(a) Individualism
(b) Ethnocentrism
(c) Culture of objectivity
(d) Cultural relativism
Ans. (d)
7. Who among the following treated magic as a ‘Pseudoscience’?
(a) Taylor
(b) Frazer
(c) Morgan
(d) Malinowski
Ans. (b)
8. According to T. Parsons, there are three modes of motivational orientation. Which one of the following is not included in these modes?
(a) Cognitive orientation
(b) Cathertic orientation
(c) Appreciative orientation
(d) Evaluative orientation
Ans. (c)
9. Clark Wissler demonstrated that in each restricted area of a culture, a central point of dispersal could be identified. People living on the borders of two culture areas share the features of both.
Such areas are called:
(a) Areas of cultural parallels
(b) Areas of cultural similarities
(c) Areas of cultural amalgamation
(d) Marginal areas
Ans. (d)
10. The fact that diffusion is possible shows that:
(a) Evolution is a mistaken doctrine
(b) Societies have fixed genetic constitutions
(c) Evolution cannot be precisely unilinear
(d) Progress is inevitable
Ans. (c)
11. Which one of the following covers the situation where a TV commentator continues to describe a cricket match as a radio commentator would?
(a) Diffusion
(b) Cultural lag
(c) Communication gap
(d) Technological lag
Ans. (d)
12. Ethnocentrism refers to:
(a) Appreciating cultural traits of other groups
(b) The tendency of a cultural group to uphold and sustain traditional culture
(c) The attitude that one’s own culture or group is superior to another
(d) The attempt to modernise traditional cultural values
Ans. (c)
13. According to T. Parsons, behaviour becomes action when four conditions are present. Which among the following condition is not one of them?
(a) Orientation to attainment of ends
(b) Occurrence in particular situations
(c) Being regulated by norms and values of the individual actor
(d) Involvement of an emotional investment of energy
Ans. (d)
14. Which one of the following is a social relationship?
(a) Two armies facing each other
(b) Thirty candidates seated in an examination hall
(c) People running for shelter during a sudden downpour
(d) Cinema viewers and actors on the screen
Ans. (a)
15. A man, who has accumulated a lot of black money, constructs a hospital for cancer patients and poses himself as a savior of the downtrodden. This is an example of:
(a) Role insulation
(b) Counterfeit role
(c) False role
(d) Role-set
Ans. (b)
16. Diachronic orientation in cultural analysis is not present in the theories of:
(a) Historical particularism
(b) Evolutionism
(c) Diffusionism
(d) Structuralism
Ans. (a)
17. Who among the following is not a contributor to the studies on acculturation?
(a) Linton
(b) Redfield
(c) Herskovits
(d) Ogburn
Ans. (d)
18. Who among the following drew a distinction between social structure and structural form?
(a) Radcliffe-Brown
(b) S.F. Nadel
(c) Edmund Leach
(d) Evans-Pritchard
Ans. (a)
19. Structural differentiation refers to:
(a) Progressive specialisation and autonomous functioning of social units
(b) Changes in the structural forms of social units
(c) The process of evaluation and ranking of social institutions
(d) The proliferation of social units
Ans. (a)
20. Who among the following held the view that we cannot talk social structure in the singular?
(a) Levi-Strauss
(b) Meyer Fortes
(d) Talcott Parsons
Ans. (c)
21. Summer referred to his model of society as a:
(a) Developmental model
(b) Conflict model
(c) Consensus model
(d) Progressive model
Ans. (d)
22. Consider the following characteristics:
1. A network of social relationships
2. Totality of population
3. Provision for membership by birth
4. Comprehensive culture
The major characteristics of society would included
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
23. Merton speaks of three characteristics of a group and group membership. According to Merton, which one of the following is not a characteristic of social group?
(a) Frequency of social group
(b) Interacting persons defining themselves as members
(c) Persons in interaction being defined by others as belonging to the group
(d) Intended all social activities
Ans. (d)
24. Which one of the following constitutes a primary group?
(a) All inmates of a prison
(b) Sugarcane plantation workers
(c) Members of Alcoholics Anonymous of a metropolis
(d) Mother and her three children
Ans. (d)
25. A group which does not allow a person to join similar other, groups at one and the same times is called:
(a) Disjunctive group
(b) Overlapping group
(c) Exclusive group
(d) Congregate group
Ans. (a)
26. Who held the view that the primary groups are ‘the breeding grounds of our mores and the nurse of our loyalties’?
(a) Cooley
(b) Tonnies
(c) Maclever
(d) Sumner
Ans. (c)
27. Consider the following elements:
1. Identified goals
2. Ascribed roles
3. Membership for life
4. Voluntary membership
5. Authority structure
6. A set of rules
Which of these are elements of a complex organisation?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 5 and 6
(d) 1, 4, 5 and 6
Ans. (d)
28. Consider the following functions:
1. Aiding a member’s entry into the group
2. Easing the member’s adjustment after he has become a part of the group
3. Strengthening the member’s position within the membership group
4. Reducing the member to being a ‘marginal man’
According to Merton, which of these are the twin functions served by anticipatory socialisation?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans. (c)
29. The negative reference group has been studied by:
(a) Harry Johnson
(b) Ralph Linton
(c) Theodore Caplow
(d) William Scott
Ans. (c)
30. Status inconsistency refers to:
(a) Differential ranking on the dimensions of social stratification
(b) Discrepancy and conflict in the status and role of an individual
(c) Gaps between expectation and performance
(d) Incompatibility among the different status of an individual
Ans. (d)
31. Who among the following defined social institutions as the social structure and machinery through which human society organises, directs and executes multifarious activities required to satisfy human needs?
(a) E. A. Ross
(b) K. Davis
(c) C.H. Copley
(d) H.E. Barnes
Ans. (d)
32. According to Durkheim, which one of the following is a prerequisite of modern economic development?
(a) Collective conscience
(b) Collective representations
(c) Mechanical solidarity
(d) Organic solidarity
Ans. (d)
33. That society passes from the sacred to the secular stage is an idea expounded by:
(a) David Riseman
(b) Howard Becker
(c) Max Weber
(d) Karl Marx
Ans. (a)
34. The maxim that a culture must be understood and evaluated on its own terms without reference to the values of another culture, is known as:
(a) Cultural hegemony
(b) Cultural relativism
(c) Cultural plutalism
(d) Cultural specificity
Ans. (b)
35. Assertion (A): Concept of culture suggests boundedness, homogeneity, coherence and stability.
Reason (R): Social reality is characterised by variability, inconsistencies and individual agency.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (b)
36. Assertion (A): Under the influence of mass-culture, people support the prevailing system of domination, against their own interest.
Reason (R): The mass-culture promotes apathy, resignation and acceptance of things as they are.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
37. Assertion (A): Society always tries to come out with solution to overcome a problem.
Reason (R): No society can afford to let a problem continue lest its unity and survival are endangered.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
38. Assertion (A): Nordic race is superior and creates superior culture.
Reason (R): A super-race does not create superior culture.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (d)
39. The book Sociology of Economic Life was written by:
(a) A. Etzioni
(b) J. Shumpeter
(c) Neil J. Smelser
(d) M.Weber
Ans. (c)
40. Which one of the following sets of tribes belongs to Southern Kinship zone according to Irawati Karve?
(a) Korku, Gond and Bhil
(b) Bhil, Kadar and Koya
(c) Koya, Gond and Oraon
(d) Kadar, Coorgi and Khasi
Ans. (b)
41. Who among the following said that the approach to human development encompasses jnana, karma and bhakti?
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Swami Vivekananda
(c) Amartya Sen
(d) Murari Bapu
Ans. (b)
42.
On the basis of the given kinship diagram those who are not parallel cousins would include:
(a) L, M, Q and S
(b) N, P, T and U
(c) Q, R, K and M
(d) K, L, M and O
Ans. (d)
43. Male primogeniture form of succession and inheritance was practiced among the
(a) Marathas
(b) Nayars
(c) Brahmins of Karnataka
(d) Namboodiri Brahmins
Ans. (d)
44. Irawati Karve speaks of four-clan rule, practiced in North India in mate selection restrictions. Which one of the following is not included in the four-clan rule?
A man must not marry a woman from his-
(a) Father’s gotra
(b) Mother’s gotra
(c) Father’s mother’s gotra
(d) Mother’s father’ gotra
Ans. (d)
45. Genetic characteristics are evident among:
(a) Affinal kins
(b) Consanguineal kins
(c) Unilateral kins
(d) Bilateral kins
Ans. (b)
46. ‘Marriage is said to be essential for women because that is the only sacrament performed by them’. According to:
(a) P. H. Prabhu
(b) K. M. Kapadia
(c) P.Y. Kane
(d) A.S. Altekar
Ans. (b)
47. The statement, the ritually married husband is not necessarily the “legalised genitor” of the children born to his wife”, applied to which one of the following castes or communities in the olden times?
(a) Coorgis
(b) Namboodiris
(c) Nayars
(d) Khasis
Ans. (c)
48. P. Kolenda has given some compositional categories of nuclear family in India. Which one of the following is not one of the categories presented by Kolenda?
(a) Supplemented nuclear
(b) Sub-nuclear
(c) Single person household
(d) Supplemented lineal
Ans. (d)
49. Assertion (A): Muslims marriage, regulated by Muslims’ personal law is a social character.
Reason (R): ‘Shariat’, the personal law of the Muslim, lacks in sacramental character.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
50. Assertion (A): For matrimonial relations, upper caste people are more class conscious than being caste conscious.
Reason (R): Economic status of the family is an important factor in the settlement of marriage.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (d)
51. Assertion (A): In the opinion of Irawati Karve, caste is an extended kin-group.
Reason (R): All the members of a case believe that they have descended from a common ancestor.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (c)
52. Assertion (A): It is not correct to assume that matrilineal families are consanguineal families.
Reason (R): Besides the consanguineal kins, the tharawad of Nayars consist of official relatives also.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
53. Assertion (A): Marriage is a union between one man and one woman.
Reason (R): It establishes legitimacy of sex union and also the legitimacy of children.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
54. Assertion (A): Territorial exogamy is not strictly confined to Northern Kinship zone.
Reason (R): “Devara Okkalu” of the Gandadikar Okkaligas of Karnataka was a form of territorial exogamy.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
55. The main difference between class and status is that:
(a) The former refers to economic group and the latter to hereditary ranking of family
(b) The former is associated with ownership of means of production and the latter with styles of life
(c) The former refers to personal power and the latter is associated with privileges that one enjoys
(d) The former refers to acquisition of political power and the latter to gain of social power
Ans. (b)
56. Consider the following statements:
Social stratification is
1. A hierarchical division of society
2. Based on cultural background of the people
3. A contractual system of division of society into groups
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 only
(d) 3 only
Ans. (a)
57. Consider the following sociologists:
1. Pierre van der Berghe
2. Kingsley Davis
3. Melvin Tumin
4. Gerhard Lenski
Who among these sociologists attempted a reconciliation between the Marxist and the functionalist theories of social stratification?
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 3 and 4
Ans. (c)
58. Consider the following statements:
1. Language is the basis of bio-social form of differentiation
2. Age is the basis of the socio-cultural form of differentiation
3. Sex is the basis of bio-social form of differentiation
4. Religion is the basis of socio-cultural form of differentiation
Which of these statements are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans. (b)
59. Who is the author of the book White Collar- American Middle Class?
(a) John H. Goldthorpe
(b) William Foote Whyte
(c) Barbara Wooten
(d) C. Wright Mills
Ans. (d)
60. Which one of the following theories supports the view that inequality is not only endemic but also necessary?
(a) Conflict
(b) Functionalist
(c) Indological
(d) Structuralist
Ans. (b)
61. Which one of the following helps to maintain the structural distance between castes?
(b) Political power
(c) Land ownership
(d) Purity and pollution
Ans. (d)
62. Consider the following features:
1. Numerical strength
2. Economic status
3. Ritual status
4. Political power
5. Legal status
Which of these is/are not feature(s) of a dominant caste?
(a) 2 and 5
(b) 1 only
(c) 5 only
(d) 3, 4 and 5
Ans. (c)
63. In modern society, if a peasant’s son becomes a skilled worker in a city, then it is a case of:
(a) Horizontal mobility
(b) Upward mobility
(c) Downward mobility
(d) Geographical mobility
Ans. (b)
64. Consider the following caste groups:
1. Jat-Sikhs of Punjab
2. Nadras of Tamil Nadu
3. Jatavs of UP
4. Vokkaligas of Karnataka
Which of these groups have experienced upward mobility in the caste system?
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans. (d)
65. Consider the following characteristics:
1. Segmental division of society
2. Unrestricted division of society
3. Civil and religious disabilities and privileges
Which of these are the characteristics of the caste system?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3
Ans. (d)
66. The view that the Varna system is an order the Jati system is a classificatory scheme, was held by:
(a) McKim Marriot
(b) Milton Singer
(c) Andre Beteille
(d) Dipankar Gupta
Ans. (c)
67. Which one of the following pairs of sociologist said that classes develop on the basis of different positions which individuals occupy in the productive system of the society?
(a) Karl Marx and Talcott Parsons
(b) Karl Marx and Max Weber
(c) Max Weber and Dahrendorf
(d) Max Weber and Talcott Parsons
Ans. (b)
68. An untouchable getting converted to Christianity, is an example of:
(a) Horizontal mobility
(b) Vertical mobility
(c) Social mobility
(d) None of the above
Ans. (b)
69. Assertion (A): In a caste system in which the accommodation lasts for a long time, the attitudes of members of the stratified groups get adjusted to the arrangement.
Assertion (R): Accommodation is more than a purely external relationship and has become a conditioning force in shaping the social attitudes of persons.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)
70. Which one of the following tribes is a pastoral community?
(a) Apatani
(b) Baiga
(c) Mishmi
(d) Toda
Ans. (d)
71. That socialism could completely avoid the organisational characteristics of industrialism was denied by:
(a) Daniel Bell
(b) Max Weber
(c) Gunnar Myrdal
(d) David Harvey
Ans. (d)
72. What is Daniel Bell’s axial principle with reference to the class structure?
(a) Supremacy of political elites
(b) Growing power of bureaucrats
(c) Supremacy of professional and technical occupations
(d) Supremacy of academic elites
Ans. (c)
73. Consider the following states:
1. Maharashtra
2. Tamil Nadu
3. Rajasthan
4. Bihar
The correct sequence of these States in descending order in terms of the percentage of persons below the poverty line, is
(a) 4, 2, 3 and 1
(b) 4, 2, 1 and 3
(c) 2, 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 4, 3 and 1
Ans. (b)
74. Which one of the following is not a reason for the increasing rates of unemployment in India?
(a) Economic recession.
(b) Increasing use of micro-electronics in industry
(c) Major tilt in government policy
(d) Doctrine of Karma
Ans. (d)
75. Who among the following has supported the maintenance of cottage and small-scale industries in capital-poor countries with a dense rural population?
(a) Adam Smith
(b) M.J. Levy
(c) C. P. Kindleberger
(d) W. Arthur Lewis
Ans. (c)
76. What is the latent function of the institution of potlatch?
(a) Ostentatious display of wealth
(b) Non-rational use of economic resources
(c) Sustained economic activity
(d) Maintenance of Kinship patterns
Ans. (a)
77. For development of modern capitalism, it is necessary to have:
(a) Formal and value rationalities
(b) Formal and instrumental rationalities
(c) Instrumental and value rationalities
(d) Instrumental rationality
Ans. (b)
78. The process of production requires four factors, namely, land, capital, labour and entrepreneurship, according to:
(a) Maclver and Page
(b) Marx and Engels
(c) Parsons and Smelser
(d) Roethlisberger and Dickson
Ans. (c)
79. Which one of the following tribes is associated with the Bhagat Movement?
(a) Seharia
(b) Bonda
(c) Bhil
(d) Mina
Ans. (b)
80. Assertion (A): Commercial revolution was the main reason for the development of medieval cities.
Reason (R): Colonisation and conquests opened up the East to the Western market.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (b)
81. Robert Park and Burgess arranged modern cities in a series of the following concentric zones:
1. Commuters zone
2. Zone in transition
3. Central business district
4. Zone of working population
5. Residential zone
According to Park and Burgess, the correct sequence of these five concentric zones starting from the centre and going outward is:
(a) 3, 4, 2, 5 and 1
(b) 3, 2, 4, 5 and 1
(c) 3, 5, 1, 4 and 2
(d) 4, 5, 2, 3 and 1
Ans. (b)
82. Which one of the following approaches of urban study refers to the concentric zones of modern city growth?
(a) Zonal
(b) Sectoral
(c) Geographical
(d) Ecological
Ans. (c)
83. When urban population grows and the proportion of urban population to the total population remains constant, is known as:
(a) Urbanisation
(b) Over-urbanisation
(c) Urban grow
(d) Population stability
Ans. (c)
84. According to Robert Blauner, there is X between the level of technology used and alienation, X stands for
(a) An equal relationship
(b) An inverse relationship
(c) A positive relationship
(d) No relationship
Ans. (c)
85. According to the studies available, which one of the following has remained the most effective factor of social change amongst the Dalits?
(a) Reservations
(b) Social reforms
(c) Industrialisation
(d) Collective action
Ans. (d)
86. Which one of the following groups of thinkers belong to the linear view of social change?
(a) Comte, Pareto and Marx
(b) Pareto, Sorokin and Ogburn
(c) Comte, Ogburn and Marx
(d). Comte, Spencer and Pareto
Ans. (c)
87. Which one of the following figures showing age-sex pyramid is typically characteristic of developing countries?
Ans. (d)
88. Based on the 1981 -91 decennial growth rate of population. States with the highest and the lowest growth rates are respectively:
(a) Arunachal Pradesh and Goa
(b) Nagaland and Kerala
(c) Arunachal Pradesh and Kerala
(d) Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu
Ans. (b)
89. Consider the statistics presented in the following table:
Based on the above data, which one of the following pairs of States will have the lowest fertility rate?
(a) I and III
(b) II and III
(c) I and IV
(d) II and IV
Ans. (c)
90. Consider the following reasons:
1. Birth-rate has not changed at all over the past 50 years
2. Although birth-rate has declined, the declined in death rate has been faster
3. While the birth-rate has been declining, death rate has stagnated over time
4. Decline in death rate preceded the decline in birthrate by almost half a century
Which of these are the reasons for the rapid growth of population in India?
(a) 2 and 4
(c) 1 and 4
(c) 1 and 4
(d) 3 and 4
Ans. (a)
91.
The correct arrangement of States marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the given map in terms of ascending order of percentage of literates in these States is:
(a) 2, 3, 4 and 1
(b) 3, 2, 1 and 4
(c) 3, 2, 4 and 1
(d) 2, 3, land 4
Ans. (a)
92. Which one of the following political movement mobilised its support on the basis of caste loyalties?
(a) Self-respect movement
(b) Naxalite movement
(c) Kisan movement
(d) Bodo movement
Ans. (a)
93. Which one of the following is the correct arrangement of States marked as 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the given map in terms of descending order of population density per square kilometre?
(a) 4, 3, 2 and 1
(b) 4, 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2, 4 and 3
(d) 2, 3, 1 and 4
Ans. (b)
94. Assertion (A): Quality of life in Indian cities is poor.
Reason (R): Large number of poor people live in Indian cities.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true
Ans. (b)
95. Coercion refers to:
(a) Use of physical force to gain one’s interest
(b) Large-scale violence leading to disruption of social life
(c) Prevalence of warring groups in society
(d) Social interaction in which one person or group forces its will on another
Ans. (d)
96. Routinisation of charisma refers to:
(a) The process by which the personal qualities of a charismatic leader are incorporated in the characteristics of an organisation
(b) The wide acceptance of the leadership quality of the charismatic leader by his followers
(c) The high normative standard of the actions of charismatic leader
(d) The ultimate goal which the charismatic leader has attained
Ans. (a)
97. Which one of the following is common to classes, estates and castes?
(a) Hierarchically arranged income groups
(b) Hierarchically arranged strata
(c) Hierarchically arranged hereditary groups
(d) Horizontal strata typical of certain societies.
Ans. (b)
98. Consider the following:
1. Hierarchy
2. Ascribed status
3. Goals
4. Impersonal relations
5. Compensation in kind
Which of these are the traits of an industrial bureaucracy?
(a) 1, 3 and 4
(b) 2, 4 and 5
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 4 and 5
Ans. (a)
99. The women of Bishnoi community hugged the free to prevent the woodcutters from cutting the trees to build a palace in:
(a) Gujarat
(b) Haryana
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Ans. (c)
100. Which one of the following refers to a system in which the central element is an elected legislative body whose laws are implemented by executives who are a part of an organised bureaucracy?
(a) State system
(b) Acephalous system
(c) Political democracy
(d) Socialism
Ans. (c)
101. Which one of the following is institutionalised and involves the right to take certain actions including decisions to issue commands?
(a) Authority
(b) Force
(c) Power
(d) Influence
Ans. (a)
102. Which one of the following is based on the belief in the sanctity of habit and obedience to a person who occupies a customary position of authority?
(a) Feudal authority
(b) Traditional authority
(c) Charismatic authority
(d) Legal authority
Ans. (b)
103. Who among the following is an advocate of the theory of Civil Legitimacy?
(a) John Locke
(b) Thomas Hobbes
(c) J.J. Rousseau
(d) Aristotle
Ans. (c)
104. Who among the following expressed the view that leadership necessarily required an element of voluntary submission on the part of the followers?
(a) Marx
(b) Weber
(c) Bottomore
(d) C. Wright Mills
Ans. (b)
105. The first person or set of the persons to have used the term ‘Political Socialisation’ was:
(a) Herbert Hymon
(b) Herbert Spencer
(c) Almond Powell
(d) Easton and Dennis
Ans. (a)
106. The status of organisations like the FICCI and CII in the political system is that of a/an:
(a) Economic institution
(b) Trade association
(c) Pressure group
(d) Interest group
Ans. (c)
107. According to Engels:
(a) A women’s work never gets done
(b) Women are the last to be hired and first to be fired
(c) Women constitute a reserve labour force
(d) Women can only be a seasonal labour force
Ans. (c)
108. Assertion (A): Minorities in India feel insecure and alienated.
Reason (R): Minorities are ethnocentric.
(a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not a correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a)