ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Casteism in India: Definition, Characteristics and Causes!
Essay # Definition of Casteism:
“Casteism is loyalty to the caste translated into politics”. —D.N. Prasad
“Casteism………. is an over-riding, blind and supreme group loyalty that ignores the healthy social standards of justice, fair play, equity and universal brotherhood”. —Kaka Kalelkar.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
“In this way it is only because of casteism that the Smiths want to benefit only the Smiths while the Joneses want to come to the aid of other Joneses. It matters little if the members of the other castes are irreparably harmed, if it does not cause any concern to the Smiths and Joneses”. —K.M. Panikkar
It is clear from the above definitions that casteism is a blind group loyalty towards one’s own caste or sub-caste which does not care for the interests of other castes and their members.
Essay # Characteristic Features of Casteism:
1. Casteism ignores and does not care for the interests of other castes. It signifies blind caste or sub-caste loyalty.
2. It ignores the human values and social welfare.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. It hinders the spirit of democracy. It is anti-democratic.
4. It plays a nasty role in elections.
5. As regards casteism. Prof. M.N. Srinivas says, “on a short term basis the country is likely to have more trouble with caste”.
6. It is against the ideal of Indian constitution.
7. It hinders the process of national integration.
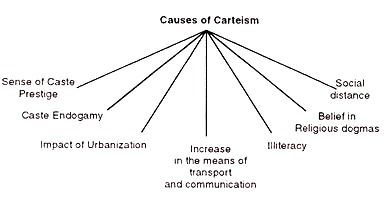
Essay # Causes of Casteism:
1. Sense of Caste Prestige:
It is the most important cause of casteism. Feeling of own caste superiority over other castes Is the main factor. It is people’s strong desire to enhance caste prestige. Members of a particular caste or sub-caste have the tendency of developing loyalty to their own caste.
Each and every member tries to keep up their caste prestige and superiority over other castes intact. This type of loyalty towards the caste makes the members of the caste in favour of their own members of the caste wherever they get the opportunity. It leads to casteism.
2. Caste Endogamy:
Caste endogamy refers to marriage within the same caste. Caste endogamy is therefore responsible for the emergence of the feeling of casteism. Individuals are more prone to develop their loyalties towards their own caste and sub-caste people. The practice of endogamy makes the people narrow-minded.
3. Impact of Urbanisation:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Urbanisation indirectly favouring casteism. Due to the impact of industrialization people migrate from the rural areas to urban areas. When they go to a new place, naturally they search for their caste people. They consider their own caste people as their own potential friends and well-wisher. Hence it leads to strengthen caste feeling and casteism.
4. Increase in the Means of Transport and Communication:
Advancement and improvement in the means of transport and communication leads to a better organisation of caste. The feeling of casteism is also rapidly propagated through the medium of newspapers.
5. Illiteracy:
Lack of literacy leads to narrow-mindedness. Mostly the illiterate people have more caste feelings. Hence it leads to casteism.
6. Belief in Religious Dogmas:
Due to illiteracy, people are governed by belief in religious dogmas, blind beliefs and superstitions. Due to the practice of ‘Jati Dharma’ they take interest in their own caste. It leads to caste feeling and casteism.
7. Social Distance:
Specially in rural areas, people belonging to the higher caste maintain social distance from the lower castes. They maintain it through different restrictions like inter-caste mintages, Inter-dinning etc. The ideologies of an individual tire conditioned exclusively by his caste norms and values. This has given rise to casteism.